What are the symptoms of an acquired brain injury?
Acquired brain injury causes symptoms similar to those suffering from a traumatic brain injury. Symptoms include headaches, dizziness, fatigue, memory loss, and depression. The type of rehabilitation an acquired brain injury patient will require depends on the severity of the brain injury. There are different types of rehabilitation available, which will depend on how severe the brain injury is.
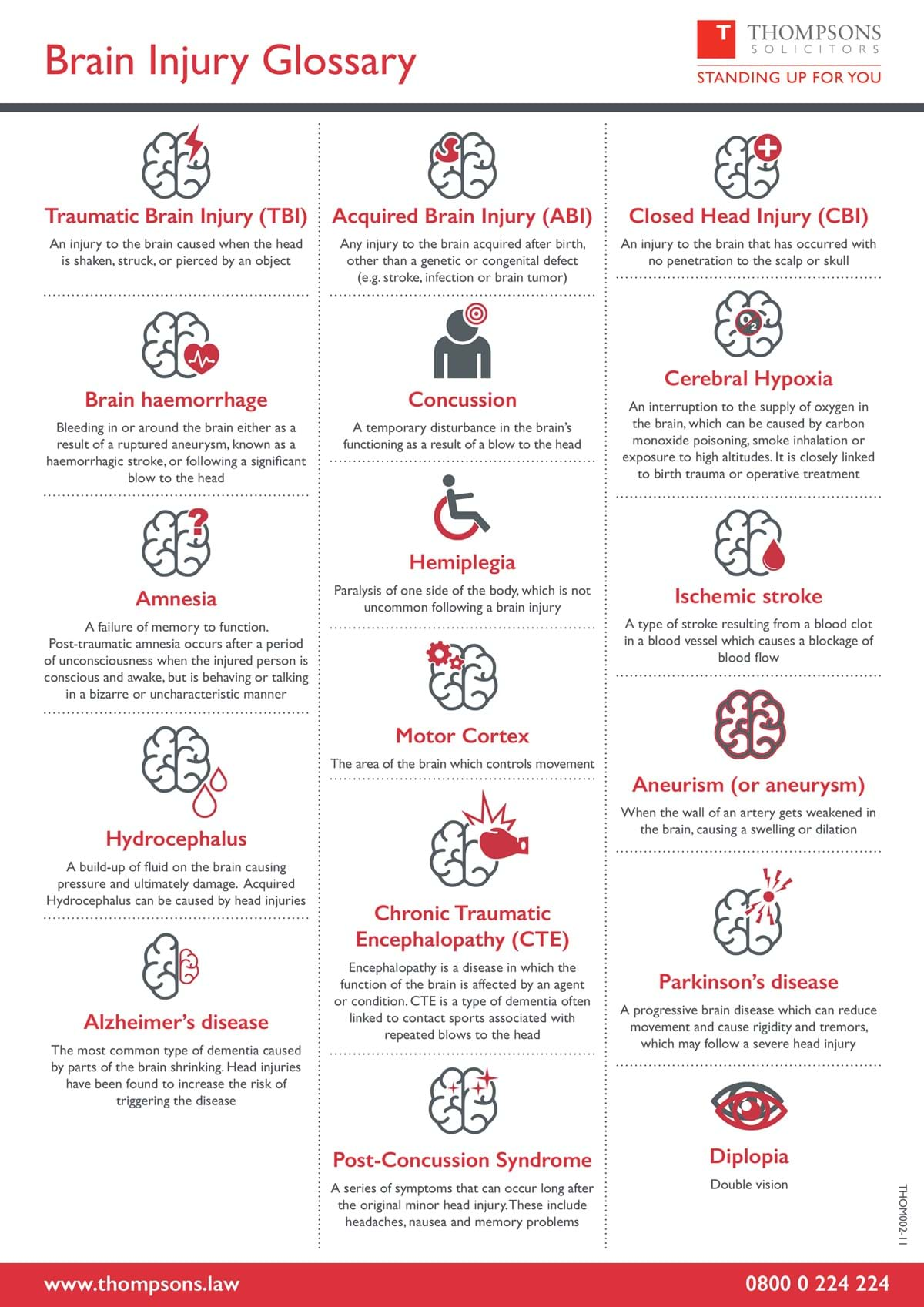
Amnesia
Amnesia is a failure of memory recall. Post-traumatic (anterograde) amnesia can occur after a period of unconsciousness. Sometimes amnesia affects both before (retrograde amnesia) and after the traumatic event or condition. The length of time memory is affected usually depends on the severity of the brain injury.
Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia caused by parts of the brain shrinking. Research into Alzheimer’s and its possible causes continues.
Brain haemorrhage
A brain haemorrhage is bleeding in or around the brain either as a result of a ruptured aneurysm, known as a haemorrhagic stroke or following a significant blow to the head.
Cerebral hypoxia
Cerebral hypoxia is an interruption to the supply of oxygen in the brain. A lack of oxygen can have many different causes.
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE)
Encephalopathy is a disease in which the function of the brain is affected by an agent or condition. CTE is a type of dementia and can be linked to repeated injuries to the head.
Closed head injury (CBI)
A closed head injury is an injury to the brain that has occurred with no penetration to the scalp or skull.
Concussion
A concussion is a temporary disturbance in the brain’s functioning as a result of a blow or violent and abrupt shake/jolt to the head.
Is a concussion a brain injury?
A concussion is a mild and temporary traumatic brain injury. Most concussion symptoms can be treated at home. However, you should seek medical advice if you have been concussed or have problems with your memory after a blow to the head.
What is post-concussion syndrome?
Post-concussion syndrome occurs long after the original blow to the head and the symptoms can include headaches, nausea and memory problems.
How long does concussion syndrome last?
There is no set time for how long it takes for concussion to pass. Symptoms, such as headaches, can last just a few days or can persist for much longer.
Can you claim compensation for concussion?
You may be able to make a claim if your concussion injuries were caused in an accident that wasn’t your fault or by someone else’s negligence. Find out more about making a concussion claim on our brain injury claims page.
Diplopia
Diplopia is another word for double vision, which is when you look at one object but can see two images. Double vision can occur in one or both eyes and can happen as a result of an injury to the head.
Hemiplegia
Hemiplegia is a form of paralysis on one side of the body it can occur after a brain injury, particularly a stroke. It can affect mobility and cause muscle weakness, including incontinence.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a build-up of fluid on the brain causing pressure and ultimately damage. Acquired Hydrocephalus can be caused by a head injury.
Ischemic stroke
Ischemic stroke is a type of stroke resulting from a blood clot in a blood vessel which causes a blockage of blood flow.
Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive brain condition which can reduce movement and cause rigidity and tremors. The precise cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown.
Post-concussion syndrome
Post-concussion syndrome is a series of symptoms that can occur long after the original concussion injury. Symptoms may include fatigue, dizziness, headaches, nausea and memory problems.